The world of Fluorite: The Colorful Mineral
Share
Welcome to the World of Fluorite, the colorful mineral.
Enter the enchanting world of fluorite, a mineral that attracts attention with its striking color and versatile nature. Known as fluorspar among connoisseurs, this mineral is prized by the astute scientist and the intuitive spiritual seeker alike. In this in-depth exploration we unravel fluorite's properties, its uses, its geological occurrence and its spiritual significance.

What is Fluorite?
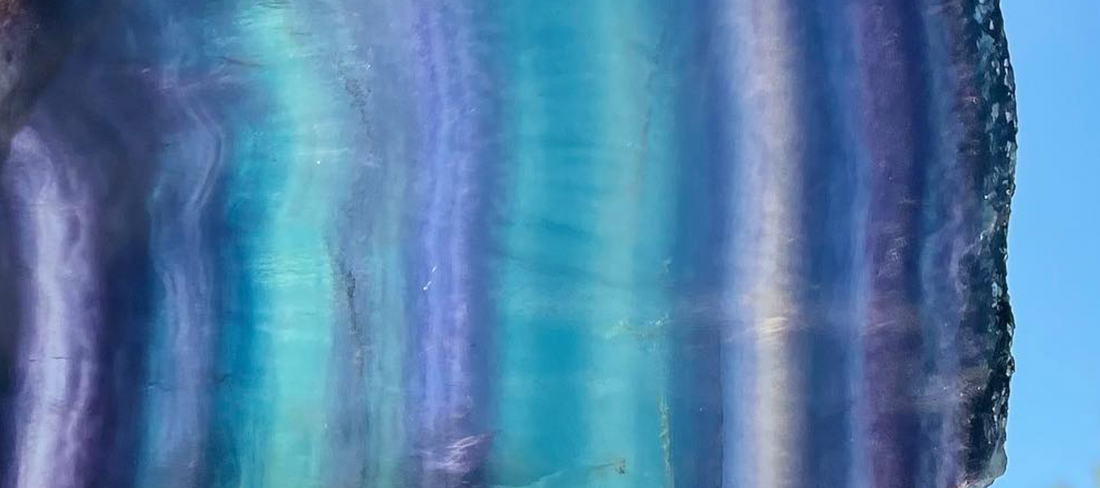
Fluorite, or calcium fluoride (CaF2), belongs to the mineral group Halides and is a mineral that presents itself in a rainbow of colors. From deep green to royal purple, from ocean blue to sunny yellow, and even to a clear, colorless transparency - fluorite's variety is a natural wonder in itself. This colorful diversity makes it a beloved object among collectors and gives it a range of optical and physical properties. With a glassy luster and perfect octahedral cleavage, fluorite can cleave into eight planes of equal directions, a characteristic that makes the mineral a fascinating study.
- Isometric Cubic Habit : Fluorite often crystallizes in an isometric cubic shape, but it is not limited to this shape. It can also take octahedral shapes and even more complex isometric shapes, adding to the mineral's variety and aesthetic appeal.
- Crystal Twins : Fluorite can exhibit crystal twins, where two crystals grow together in a symmetrical manner, adding complexity to the observed crystal habits.
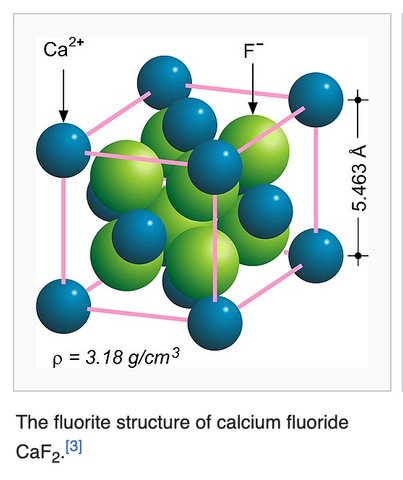
Crystal structure of Fluorite: source Wikipedia

A Name with Flow
The origin of the name 'fluorite' takes us back to early forges and metalworking, where it served as a flux to make metals flow and flow more easily. Flux is a substance introduced during the smelting of ores to promote fluidity and to remove unwanted impurities in the form of slag. The Latin ' fluere' , meaning 'to flow', gave the mineral its name and reflects a long history of practical use. Georgius Agricola, a 16th century German mineralogist, was the first to use the name, and it has since become synonymous with the bright colors and glassy luster we appreciate in fluorite today. This mineral is also the namesake of the element fluorine, as it is a vital source of fluoride ions, essential for the manufacture of hydrofluoric acid and many other fluorine compounds.

Georgius Agricola
A Geological Journey
The geological occurrence of fluorite is a story full of variation and contrast. It is mainly found in hydrothermal veins, where hot, mineral-rich waters work their way through the Earth's crust, cooling and crystallizing in the surrounding rocks. Together with other minerals such as quartz, calcite and barite, fluorite forms a palette of colors and shapes, influenced by the unique conditions of the hydrothermal fluid.
Not only in these veins, but also in pegmatites - those coarse-grained, intrusive rocks rich in rare elements - fluorite finds its place. Here it can grow into striking, often large and clear crystals. And the story doesn't stop at the solid rocks; in sedimentary rocks such as limestone and sandstone, fluorite can settle as a secondary mineral. Furthermore, it can emerge as volcanic sublimate around active volcanoes, where it crystallizes from the gas phase.
 .
. 
Of Light and Color
One of the most mesmerizing aspects of fluorite is its ability to sparkle under ultraviolet light. This fluorescent property, which gave the term 'fluorescence' to the world, shows the mineral in a different light - literally. It is the presence of certain impurities in the mineral that makes this light show possible.


Fluorite crystal in normal light and then under a UV lamp
Admired worldwide
The famous deposits of fluorite - from the green depths of England's Rogerley Mine to the sky-blue crystals of the Illinois-Kentucky Fluorspar District in the US, from the colorful varieties in China's Fujian Province to the bright blue stones of Namibia's Okorusu Mine - speak to the imagination of every enthusiast.

Rogerley Mine in England

Namibia's Okorusu Mine
Fluorite in Practice
Beyond its aesthetic allure, fluorite has proven its worth in industry and optics, where it helps to melt steel and produce the highest quality lenses. Even in the 18th century, although not recommended now, it was used as a medicine.
In gemology, fluorite is known for its wide range of colors, including purple, blue, green, yellow, colorless, and even black. This color variation, combined with the transparency and luster of fluorite, makes it a popular choice for jewelry and decorative objects.

Fluorite Donut

Fluorite bowl, museum quality
A Crystal of Meaning in the spiritual world
Known for its ability to bring order out of chaos, fluorite is valued for its cleansing and protective properties, which help ward off negative energies. It promotes mental clarity and concentration, making it a popular stone for study and professional work. This stone is associated with bringing balance and harmony, both emotionally and physically, supporting individuals in times of change. It contributes to spiritual growth by raising consciousness and strengthening intuition, making it a powerful tool for spiritual development. Fluorite is also used in healing, where it is believed to help repair physical ailments and promote self-care. The color of the stone can affect its specific properties, such as green fluorite for healing and yellow for intellect.

Conclusion
In this blog we have traveled from the deepest mines to the highest mountains, from ancient blacksmiths to modern laboratories, and through the rich landscapes of the human mind. Fluorite, in all its multi-colored glory, continues to fascinate and inspire us.
Sources: minedat and wikipedia.
You can find our offer here




